NO2 trend analysis in the U.S.
The NO2 Vertical Column Density (VCD) retrieved from Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) is commonly used in pollutant trend analysis. This research found that there is several crucial steps to ensure a fair trend analysis over a period of 10 years, such as ocean anomalies removal (systematic bias through the years) and MODIS albedo updates.
The distribution of the yearly trend of NO2 VCD is as below:
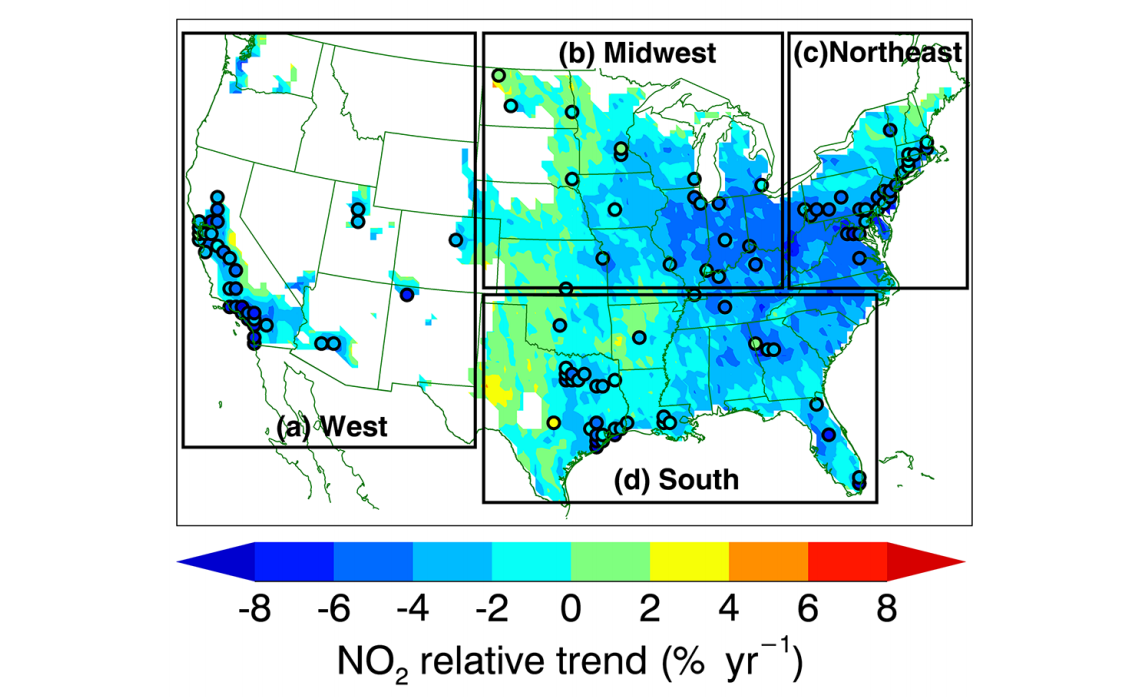
As a result, most regions have significant decreasing trends while west Texas has an increasing trend. This probably relates to the increasing petroleum industry activity.
Another interesting finding is that the relative decreasing trend is more significant in places with more NO2 base values. This may result from: 1. more effective emission control in more polluted regions or industrious regions; 2. chemical non-linearity, as NO2’s lifetime is longer when it is more abundant. Hereby, a reduction of emission (i.e., source) will leads to less NO2 in the air and shorter lifetime, resulting in the more evident decreasing trend.
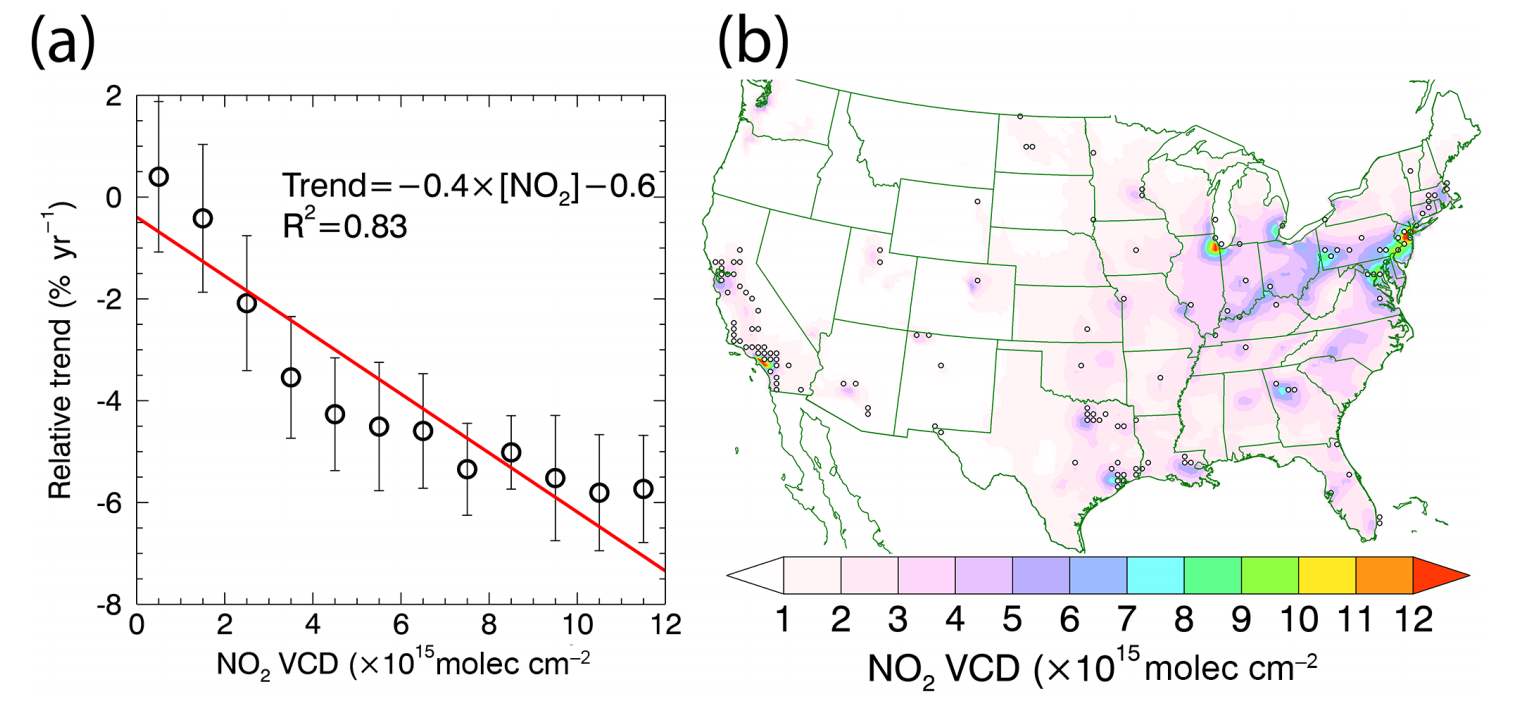
For details, please refer to the published paper: ‘Comparing OMI-based and EPA AQS in situ NO2 trends: towards understanding surface NOx emission changes’

Leave a comment